
Introduction
The debate on AI vs human intelligence continues to shape discussions in technology and education. While AI vs human intelligence benchmarks highlight AI’s superiority in structured reasoning, data analysis, and mathematical problem-solving, human intelligence remains dominant in emotional understanding, creativity, and adaptability. AI vs human intelligence assessments, such as the Mensa Norway IQ benchmarks, demonstrate how advanced AI models outperform humans in logic-based tasks. However, despite excelling in consistency and computational accuracy, AI struggles with contextual interpretation, real-world interactions, and ethical decision-making—key areas where human intelligence holds a distinct advantage. The future of AI vs human intelligence lies in hybrid collaboration, where AI’s computational efficiency is paired with human intuition and creativity to drive innovation across science, medicine, and education.
This detailed comparison explores where large language models (LLMs) excel over human intelligence and where human cognition remains superior, offering insights into the future of AI-human collaboration.
Where LLMs Outperform Humans
1. Data-Driven Tasks
AI models thrive in fields where pattern recognition, logical structuring, and numerical computations dominate cognitive challenges. Notably:
-
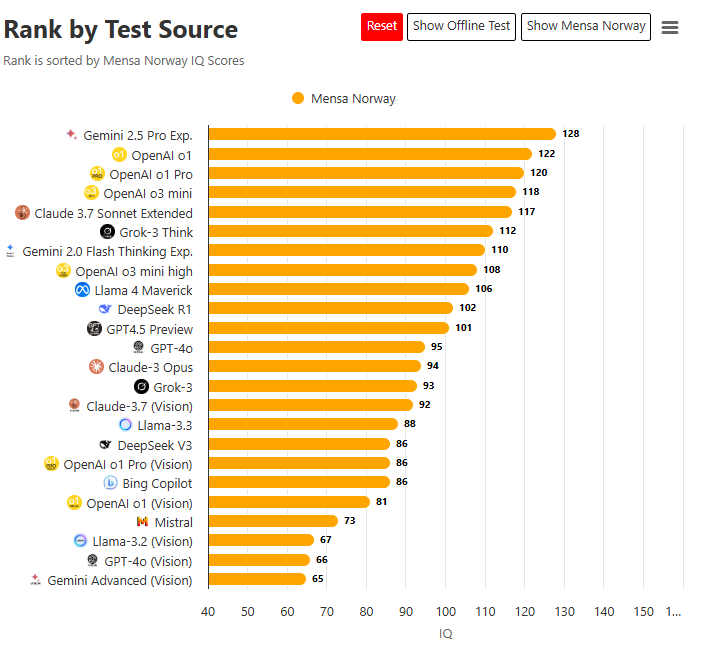
Gemini 2.5 Pro Exp. (128 IQ) solves logic puzzles and numerical sequences more accurately and efficiently than 98% of humans, outperforming traditional human reasoning in structured mathematical challenges.
-
DeepSeek R1 (102 IQ) exhibits exceptional performance in mathematical proofs and code debugging, helping programmers and mathematicians streamline computations and error-check complex equations at speeds no human could match.
In domains requiring rapid data processing, computational accuracy, and structured reasoning, LLMs far exceed human capabilities.
2. Consistency & Cognitive Stamina
Unlike humans, AI models do not suffer from fatigue or cognitive decline when performing repetitive tasks. While human problem-solving ability fluctuates based on mental exhaustion, emotional states, or distractions, AI maintains peak efficiency indefinitely. For example:
-
LLMs streamline legal document analysis, contract drafting, and repetitive cognitive tasks that require sustained attention and accuracy.
-
AI-driven automation can perform extensive scientific calculations without errors, ensuring precision in research-oriented tasks.
This unwavering consistency makes AI a superior tool for reliability-dependent fields, such as finance, law, and industrial automation.
3. Multilingual Mastery
Another significant area where LLMs outperform human cognition is in multilingual proficiency:
-
While not directly IQ-tested, models like Claude 3.7 Sonnet Extended process 50+ languages fluently, executing real-time translations and multilingual communication tasks that even polyglots struggle to perfect.
-
AI-driven language learning assistants can analyze syntax, grammar, and semantic nuances across multiple languages in ways that native speakers may struggle to replicate.
This exceptional linguistic adaptability makes AI an ideal tool for global communication, academic translation, and real-time multilingual data processing.
Where Humans Retain the Edge
1. Contextual Understanding
While LLMs excel in structured reasoning, human intelligence thrives in contextual interpretation:
-
Humans interpret sarcasm, cultural nuances, and metaphors with ease, whereas even advanced AI models like Grok-3 Think (112 IQ) frequently misinterpret abstract or emotion-laden phrases.
-
Subtle linguistic inflections and cultural references often confuse AI-generated responses, making humans indispensable in nuanced discussions requiring intuitive contextual awareness.
2. Emotional Intelligence
Despite advancements in AI-driven empathy simulation, humans retain superiority in genuine emotional processing:
-
While therapy chatbots mimic empathetic responses, they lack true moral agency, lived experiences, or authentic emotions—elements central to human emotional depth.
-
Human connections rely on shared experiences, emotional intuition, and ethical considerations, none of which AI fully replicates.
3. General Problem-Solving Ability
Humans excel in adaptability, particularly in novel or unpredictable scenarios:
-
LLMs perform poorly when facing problems outside their training data, whereas humans innovate new solutions, improvise with limited resources, and apply experiential reasoning.
-
AI models like GPT-4o (86 IQ) often falter when presented with real-world physical tasks, such as repairing machinery, diagnosing non-standard medical conditions, or improvising in emergency situations.
4. Physical-World Interaction
Despite advancements in computer vision, human sensorimotor skills remain unmatched:
-
AI models cannot physically manipulate objects, play musical instruments with human precision, or engage in tactile experiences such as cooking, athletic performance, or surgery.
-
Even advanced vision models like Gemini Advanced (Vision) still struggle to fully replicate human spatial reasoning and physical coordination.
While AI thrives in structured digital environments, human intelligence remains dominant in real-world physical interactions.
Implications of AI-Human Cognitive Differences
1. Collaborative Potential
Instead of viewing AI as a replacement for human intelligence, we should explore collaborative AI-human problem-solving models:
-
Pairing Gemini 2.5 Pro’s pattern recognition with human creativity could revolutionize fields like drug discovery, medical diagnostics, and scientific innovation.
-
AI assists humans in data processing, while humans provide creative problem-solving expertise, leading to hybrid intelligence solutions.
2. Ethical Risks in AI Intelligence Scoring
While LLMs display superior IQ scores, their intelligence is based purely on logical reasoning rather than ethical judgment:
-
Grok-3’s AI training data contains inherent biases, affecting AI-driven decision-making in legal, ethical, and societal contexts.
-
AI must be carefully regulated to avoid algorithmic biases, misinformation risks, and ethical blind spots in automated systems.
3. Redefining Education in the AI Era
The rise of AI-driven automation urges educational institutions to rethink traditional learning strategies:
-
As AI models like OpenAI o1 (122 IQ) automate rote memorization, human learning must shift toward critical thinking, ethical reasoning, and emotional resilience.
-
Future curricula must integrate AI literacy, preparing students for AI-assisted careers and hybrid intelligence applications.
The Future of Intelligence: AI & Human Synergy
While AI now exceeds average human performance in structured reasoning, true general intelligence remains uniquely human. Future advancements should focus on hybrid AI-human models, merging AI-driven logic with human intuition and ethical judgment.
-
AI assists data processing and problem-solving, while humans provide creativity, ethical reasoning, and adaptability.
-
The next frontier lies in hybrid intelligence collaborations, tackling challenges like climate change, medical innovation, and global economic development.
The evolution of AI intelligence benchmarks marks a turning point in education, problem-solving, and collaborative human-AI interactions. Rather than replacing human intelligence, AI should be harnessed as an enhancement tool, unlocking unprecedented advancements in science, technology, and human development.
For a deeper dive into human-AI collaboration frameworks, visit maximumtruth.org.
Source: Mensa Norway IQ benchmarks (2024), WAIS-IV human IQ norms, and cognitive psychology studies.






